
GCSE Geography
Processes and Landforms:
Erosion is the gradual wearing away of rock, in forming coasts there are four types of erosion that cause changing cliff faces to change:
-
Hydraulic action is when the waves cause air to become trapped in holes in the rock and this pressure builds up and eventually causes the rock to break.
-
Abrasion is when rocks carried by the waves hit the cliff face causing itto erode
-
Attrition is when rocks bump into each other and get erroded.
-
Corrosion is when nartural acididic substances cause rock to erode.
Weathering is the disintergeration of rocks due to he effect of the weather. There are three types of weathering:
-
Physical weathering: When salt crystal growth occurs, salt is left on rocks after evaporation and this salt grows and casues stress in the rocks.
-
Biological weathering is when the roots of vegetation grow in crack and cause rocks to weardown
-
Chemical weathering: When subtances such as acid rain cause rock to corrode.

Erosional Landforms
Mass movement is when large sections of cliffs collapse because they are unable to stand the force of gravity. The two most common types of mass movement are slumping and rock falls. Slumping is when the base of the cliff is eroded by the sea and the top part becomes saturated with water and it can no longer stand the weight. Rock fall are when fragments of rock break of the cliff face due to weathering and fall to the base of the cliff.
Waves
-
Swash- the turbulent layer of water that washes up onto the beach after a wave breaks.
-
Backwash- is the water that rolld back after a wavebreak.
-
Wave Crest- the highest point of a wave/
-
Sediment- this is the material such as sand and gravel that is transported by the sea.
-
Wavelength- the distance between two successive wave crests.
-
Destructive waves are powerful waves that usually occur in stormy conditions they have a high frequency, strong backwash, a weak swash and and tall waves wirh steep gradient. Destrictive waves are responsible for erosion.
-
Constructive waves are calm waves which are responsible for desposition. They have a strong swash and a weak backwash, with short waves with a shallow gradient.
-
Fetch is how long the wave has stravelled, this influences the power of the wave.
Transportation
Methods of Transportation:
There are four main methods of transportation, this includes:
-
Solution: minerals are dissolved in the water and carried
-
Suspension: small particles are carried in the water, which can make the water appear cloudy.
-
Saltation: load (which is too heavy to be transported by suspension) is bounced along the sea bed.
-
Traction: Pebbles and larger sediment are rolled across the sea bed.
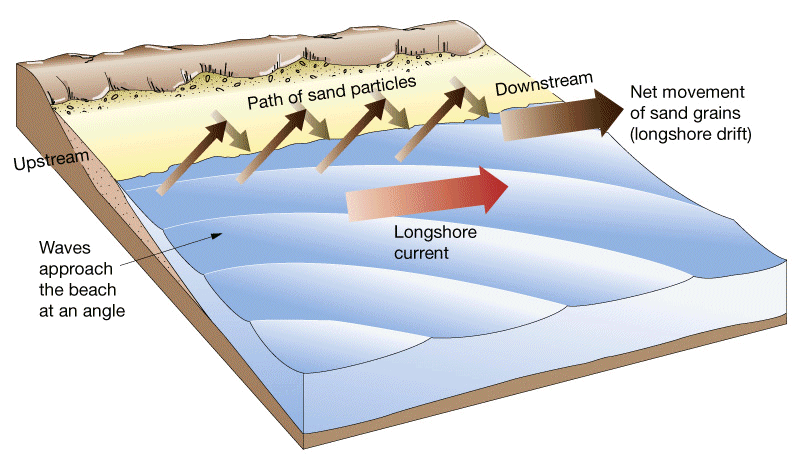
Lonsgshore Drift
Longshore drift is the transportation of sediment up a beach. Longshore drift occurs when the wave comes into the coastline at an angle which is determined by the prevailing wind. The backwash picks up sediment and brings it out and the swash brings it back in another angle, then the backwash brings it back out, this zig- zag motion continues until the shape of the coastline changes (i.e. river estuary) the wind stops.
Formation of a Spit:
Spits are formed when sediment that has been transported by Longshore drift gets deposited. When the coastline changes/ the material reaches the end of a coastline it gets deposited, as the wind gains and loses energy or when the wind direction changes, the waves take the sedment towards the shore, creating a hook shape. Behind a spit is calm sheltered water called a salt marsh. Spurn head in Humberside is an example of a spit.



Headlands and Bays :
Headlands and bays are formed when there are different types of Rock at a coastline. The hard, more resistant rocks erode slower than the soft less rsistant rock. The hard rock sticks out as headlands and the soft rock forms bays. After the bays form they become sheltered from erosion but the head land are more exposed to the power of the waves, this leads to the formation of arches, caves, stacks and stumps.

Caves, arches, stacks and stumps:
Stacks, stumps, Caves and Arches form in areas where there are hard resistant rock. A fault in the rock becomes eroded by hydraulic action and sbrasion to to form a cave, eventually both sides of the cave are aroded to form and arch. Over time, the top of the arch collapses to leave a stack. Subsequently the stack gets eroded by weathering to form a stump.

Wave Cut platforms:
The sea erodes (hydraulic action, abrasion, attrition and corrosion) the bottom of the cliff to create a wave cut notch, the cliff is eroded from above by the process of weathering. The notch increases in size, and eventullly the clif collapses. The backwas carries the rubble away from the cliff to create a wave cut platform which is clearly visible when there is a low tide.


More Depostional Landforms:
-
Sandunes ( Studland)
-
Tombola ( Chesil beach)


-
Bar (Slapton sands)
