
GCSE Geography
Types of plate boundaries:
Convergent plate boundary –This is where an oceanic and continental plate meet, the oceanic plate is denser so it subducts under the continental plaet, this can sometimes stimulate volcanic activity and result in earthquakes when the oceanic plate melts. Example : Chances peak volcano is on a convergent plate boundary where the North American plate (oceanic) is sinking below the carribean plate (continental).
.



Distribution of Volcanoes: Most volcanoes are located on or near plate boundaries in narrow bands. Volcanoes are extremely common on the ring of fire which is a volcanic chain around the Pacific Ocean. The Pacific Plate, an oceanic plate that forms the bed of the Pacific Ocean, is surrounded by a number of continental plates. The movement of these plates create zones of subduction (e.g. where the Pacific and Eurasian plates meet). This leads to the formation of volcanoes and the occurance of earthquakes in these areas. Some volcanoes are disparate to this general trend and occur in the middle of oceans, and example is Mauna Loa, these are hotspot volcanoes and are are a result of plumes of magma rising up through fissures in the Earth's crust.
Conservative plate boundary- This is when two plates slide past each other. This process is often not smooth and sometimes the plates get stuck, results in pressure building up in the rocks... The friction is eventually overcome and the energy is relesed in the form seismic waves and causes an Earthquake. Example St andreas fault- this is where the North American plate is moving past the pacific plate.
Divergent plate boundary- this occurs when two plates move apart due to the convection currents in the mantle in opposite directions . When this occurs new land is formed, magma rises to the ground and cools. Example: Mid atlantic ridge where the North American and Eurasian plates are moving apart.
Plate tectonics
Convection currents
The Earth's mantle is made up of molten rock which is in liquid form, this means that convection current. As the hot molten rock rises and sinks, convection currents form. The hot magma near the core is hotter and therefore lighter so it rises. As it nears the crust it becomes cooler and denser and sinks, this is a convenction current. This movement of magma causes plates to move.


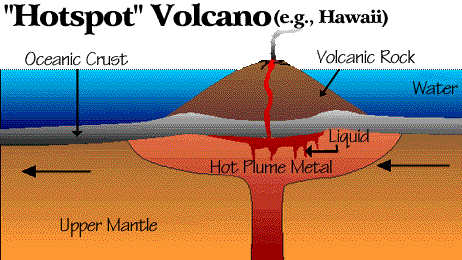
Hotspot volcanoes- Hotspot volcanoes occur in reas where hot plumes of metal rise to the surface of the crust., an example of a hot spot volcano is Mauna Loa. The hot plumes melt rock and magma rises up through fissures in the Earth's crust and slows erupts to form volcanoes. As the plate moves over the stationary hotspot, the volcano is rafted away and new ones form, this forms a chain of volcanic islands such as the Hawaiian islands. The older volcanoes become dormant or extinct.